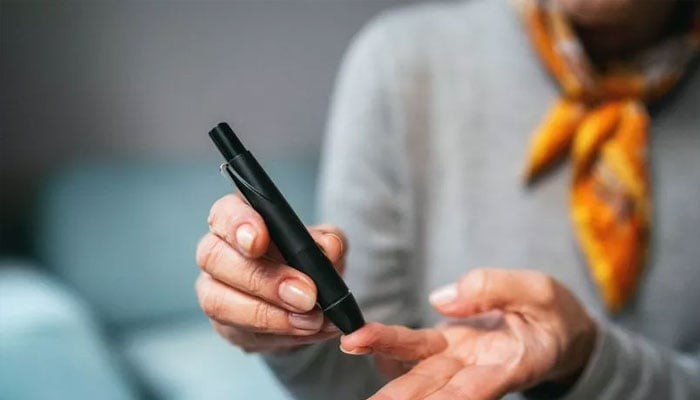
Scientist have revealed that onions, a common root vegetable, could reduce high blood sugar levels by up to 50% in diabetic patients.
The study, presented at The Endocrine Society's 97th annual meeting in San Diego revealed that extract from onion bulbs, Allium cepa, can decrease high blood glucose (sugar) in diabetic rats when examined alongside the anti-diabetic drug metformin.
"Onion is cheap and readily available and has been utilized as a nutritional supplement," said the lead researcher Anthony Ojieh, MBBS (MD), MSc, from Delta State University in Abraka, Nigeria.
He further added, "It holds potential for use in treating patients with diabetes."
Although onion extract reduced fasting blood sugar levels in diabetic rats by 50 percent and 35 percent, it also shows increase in average weight among non-diabetic rats but not diabetic rats.
"Onion is not high in calories. However, it seems to increase the metabolic rate and, with that, to increase the appetite, leading to an increase in feeding,” Ojieh said.
He further added, "We need to investigate the mechanism by which onion brought about the blood glucose reduction. We do not yet have an explanation."
Adding onions and other vegetables into your diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall well-being.