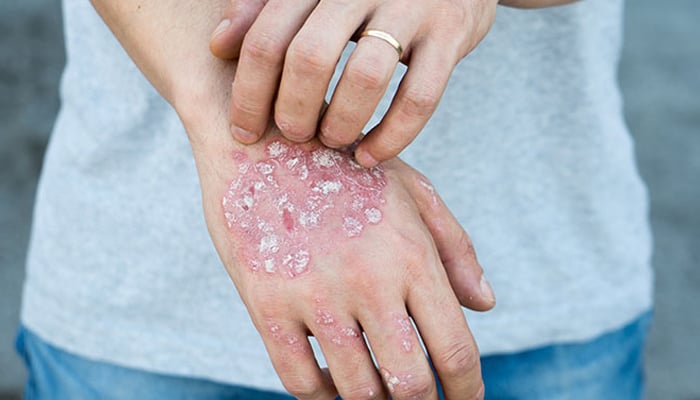
Up to 3% of adults in the U.S. are suffering from psoriasis. It’s a skin disease characterised by plaques, discolouration, and other symptoms, and it may aggravate if left untreated and
According to experts, inflammation is considered to be the most common factor that can affect these different body organs.
Inflammation in psoriasis
Psoriasis is a severe skin condition, the inflammation linked with psoriasis adversely affects the entire body.
It can increase the risk of cardiac disorders, malignancy, inflammatory bowel disorder, and more.
How to manage inflammation
While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, the following habits may help reduce psoriasis-related inflammation and increase a person’s chances of experiencing remission.
Eating a nutritious diet:
Diet is strongly associated with systemic inflammation. A recent study found that particular inflammatory dietary patterns may significantly increase the risk of psoriasis.
Here’s what you need to consume in your diet to reduce inflammation psoriasis:
Avoid inflammatory foods:
Certain beverages and foods with proinflammatory items, including ultra-processed foods, sweets, and more.
Nutrient-rich food:
Consuming nutrient-rich food such as vegetables, and fruits may minimise the risk of psoriasis.
Losing extra weight:
A study revealed that people suffering from psoriasis and obesity who reduced their weight by 12% noticed a 50–75% decrease in psoriasis complexity.
Weight loss may minimise inflammatory markers and assist reduce psoriasis in people with extra body weight.
Executing other healthy habits:
Several habits can help reduce inflammation and improve psoriasis symptoms, such as:
Quit smoking:
Smoking harms an individual’s health and aggravates inflammatory disorders, such as psoriasis.
Reducing alcohol intake:
Excessive alcohol consumption is seriously injurious to health and it may contribute to inflammation and increase the severity of psoriasis.