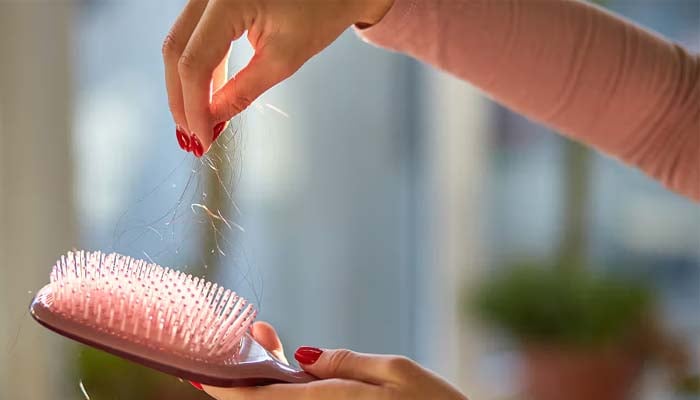
A recent study uncovered some surprising facts about the commonly consumed GLP-1 drugs that may lead to increased risks of hair loss.
For the study, scientists assessed data from nearly 550,000 adults and adolescents, including GLP-1 consumers and non-consumers.
GLP-1 drugs are often consumed to manage type 2 diabetes and promote weight loss by regulating blood sugar levels, and slowing digestion.
After a period of 12 months, researchers indicated that users were more likely to be diagnosed with telogen effluvium, a common stress-related shedding condition, and androgenetic alopecia, usually referred to as male and female pattern baldness.
The significantly higher risk remained even after contributing for sex, body mass index (BMI), age, and diabetes status.
Researchers stressed the need for more studies; however, possible causes include rapid weight loss, hormone and insulin changes, or direct effects on hair follicles.
Researchers stated, “Awareness of alopecia risk in patients on GLP-1 RAs is critical for early detection, anticipatory guidance, and multidisciplinary care.”
Notably, the study couldn’t determine the impact on teenage participants due to the absence of data.