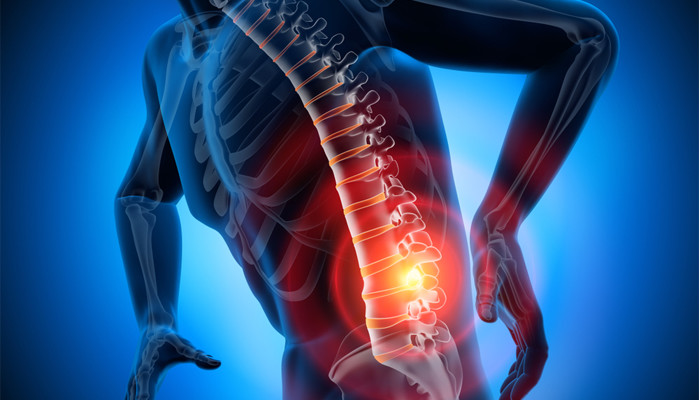
Scientists have discovered a new treatment target that can stop common side effects of spinal cord injury.
According to Neuroscience News, a study published in the journal Science Translational Research suggested that microglia cells that control abnormal nerve growth can prevent life-threatening complications.
The corresponding author of the study and executive director of Ohio State’s Belford Centre for Spinal Cord Injury, Phillip Popovich, said, “We discovered that exaggerated, life-threatening autonomic reflexes after spinal cord injury are associated with abnormal growth and rewiring of nerve fibers in the spinal cord. A specific cell type, called microglia, controls this abnormal growth and rewiring.”
He further explained, “Using experimental tools to deplete microglia, we found it’s possible to prevent abnormal nerve growth and prevent autonomic complications after spinal cord injury.”
Faith Brennan, first author of the study and a beginner of this work at Ohio State, told, “We consider this a major finding. Although this is a well-known consequence of spinal cord injury, research has mostly focused on how the injury affects neurons that control autonomic function.”
Popovich suggested, “Identifying these mechanisms could lead to the design of new, highly specific therapies to treat dysautonomia after spinal cord injury. It could also help in other neurological complications where dysautonomia develops, including multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.”