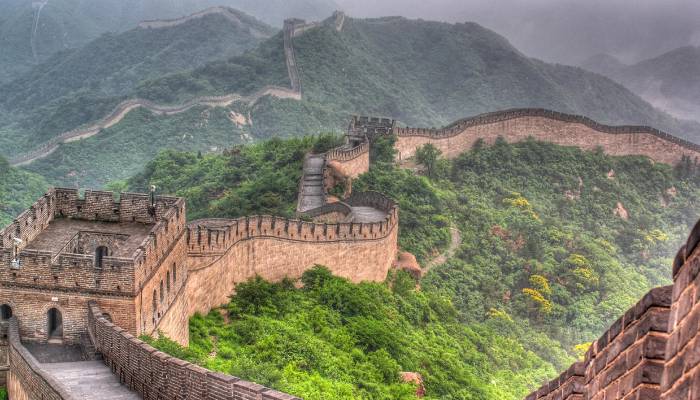
The Great Wall of China is considered one of the Seven Wonders of the World and was constructed around 2,500 years ago.
This wall is a vast military defence structure that was built over many centuries, from the 3rd century BC to the 17th century AD.
The Great Wall, spanning an impressive 20,000 kilometers along China’s northern border by successive Chinese empires.
Constructed by different rulers including Qin, Wei, Zhao, Qi, Yan and Zhongshan, its purpose was to protect the land from neighbouring kingdoms and later from northern nomadic invaders.
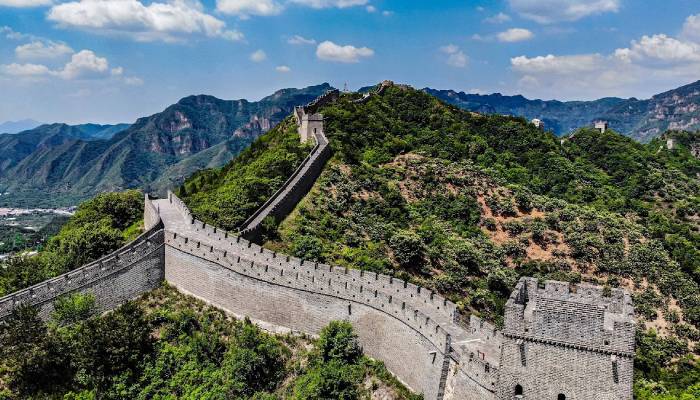

In 221 BC, Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China, united seven kingdoms to create the first Chinese empire.
To symbolize this unity, he decided to link the walls built by these kingdoms into one continuous structure.
In the start this wall was constructed using rammed earth and as the emperor changed, each contributed their own ideas for its expansion.
Over the years it grew longer, with some sections made of brick, while others used quarried granite or even marble blocks.
In 1368, Zhu Yuanzhang founded the Ming dynasty, which became renowned for its achievements, in ceramics and painting.
In this era, many watchtowers and platforms were added to the Great Wall.
As the trade grew and the Silk Road was established, the Great Wall of China served as a border control system and managing trade and also enabling taxes on goods entering or leaving the empire.