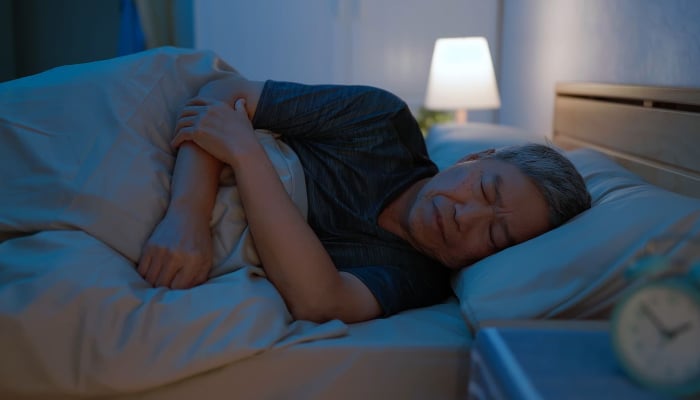
People who are habitual of oversleeping or staying in bed later than usual have a higher risk of Alzheimer's, revealed a new study.
According to Mail Online, new research has suggested that regular lying in could be a sign of numerous life-threatening diseases, including Alzheimer’s, heart disease, and diabetes.
People who sleep longer than seven hours have a greater risk of cognitive decline, while those who sleep fewer than seven hours have a lower risk of life-threatening health issues but could suffer from fatigue and poor muscle and bone health.
Related: Here are some hacks to improve quality of sleep
Professor Jianfeng Feng, biologist and co-author of the study, said, “This is a paradigm shift in how we understand the relationship between sleep and health. Our ultimate goal is to construct a comprehensive sleep health profile across the human lifespan, providing actionable insights for individuals at every stage of life.”
For this study, the researchers from the Warwick University analysed sleep data of around half a million people aged between 38 and 73. They found that lie-ins are often a sign of underlying disease rather than the cause.
The study also dismissed the finding of the previous studies that suggested that sleeping more than 9 hours could be linked to Alzheimer's disease and concluded that regular sleep of more than seven hours is a symptom of a deadly disease.
Researchers believe that the study could help in the early detection and timely treatment of the disease.
Related: How lack of sleep damages immune system? Scientists reveal shocking truth