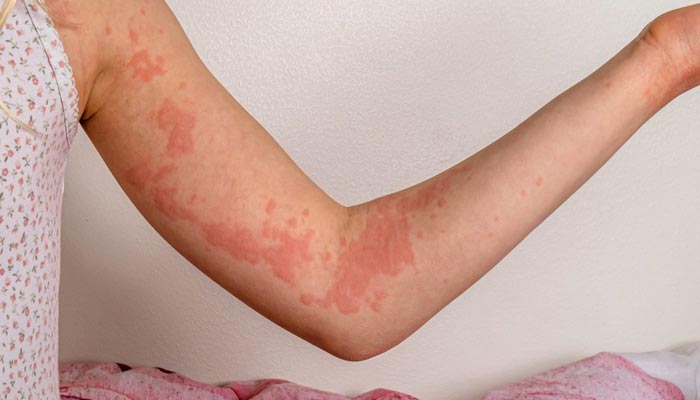
A new groundbreaking study revealed that Remibrutinib showed promising results in treating chronic spontaneous urticaria.
A recent study published in the New England Journal of Medicine outlined the potential of remibrutinib for patients suffering from symptomatic chronic spontaneous urticaria after being treated with second-generation H1-antihistamines, HealthDay reported.
Oral administration of remibrutinib, Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, was found beneficial, as it brings significant enhancement in a composite measure of hives at week 12.
Related: Regular lie-ins linked to higher risk of Alzheimer's, study
To assess the efficacy and safety of remibrutinib in patients, Charité–Universitätsmedizin Berlin MD Martin Metz and fellow researchers conducted a study.
They randomly assigned remibrutinib at a dose of 25 mg twice daily or placebo to 313 and 157 patients, in REMIX-1; 300 and 155 patients, respectively, in REMIX-2.
Eventually, researchers saw a significant improvement from baseline to week 12 in the urticaria activity during a seven-day period (UAS7).
Maximum patients in the remibrutinib group as compared to the placebo group scored 6 or lower on the UAS7 at week 12 (REMIX-1: 49.8 versus 24.8 percent; REMIX-2: 46.8 versus 19.6 percent), and a UAS7 score of 0 (REMIX-1: 31.1 versus 10.5 percent; REMIX-2: 27.9 versus 6.5 percent).
It is important to note that the adverse effects were similar in patients who were taking Remibrutinib and those who were taking a placebo.
Related: Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome: Everything you need to know