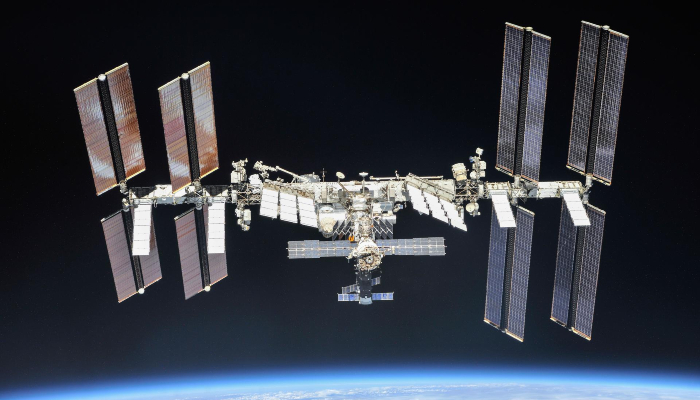
The United States is preparing to deorbit from the International Space Station (ISS) after China’s space station milestone.
According to Fox News, after seeing China’s self-sufficiency in space, the US is now also considering deorbiting from the ISS and developing its own space station.
The ISS was launched into orbit back in 1998, but before this major development, the US, along with Russia, Japan, Canada, and 11 European countries, signed an agreement for the peaceful use of the orbital laboratory.
China, who was left out of the plan after a decade, showed interest in joining the space station, but besides the European Space Agency and South Korea, the US opposed the decision.
NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy said, “I think you'll have to understand that Congress gave us very clear direction in 2011. Any bilateral cooperation with China had to be certified as not sharing any information that would give China some kind of an advantage. I think there's no question they're an economic competitor, and they're also a competitor for leadership geopolitically.”
The President of International and Space Stations at Voyager Space, Jeffrey Manber, also accepted China as a “threat” and said, “We are in a new space race.”
Moreover, China then started developing its own space station and deorbited a pair of short-term space labs between 2011 and 2018.
After launching the first part of its Tiangong Space Station, which translates to Heavenly Palace, in 2011, after almost a decade, the space station construction was completed in 2022. Since then, Beijing has been accomplishing new heights of success.
Following China’s success, NASA is now working to develop an independent space station for the US. Voyager, one of three companies contracted by NASA for the new space station, said it is planning to launch its Starlab in 2028. However, funding cuts could cause a delay.