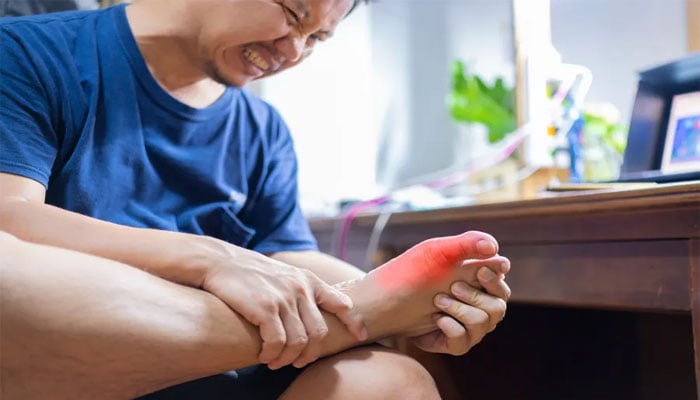
A recent study revealed that commonly prescribed drugs can easily manage gout and help in reducing the risks of cardiac attack and stroke.
As per the study published in JAMA Internal Medicine, medicines that reduce uric acid levels in the blood also minimises the risks of heart attack and stroke.
As per the scientists, common medicines such as allopurinol were discovered to be associated with enhanced cardiovascular results after consuming the correct dose.
Their heart health was compared with patients who did not reach that level.
For the study, researchers assessed health records of over 109,000 adult gout patients between 2007 and 2021.
Nearly 27% of patients accomplished the recommended uric acid target of below 6 mg/dL within a year of starting treatment.
Results indicated that patients who met the target had a 9% reduced risk of cardiac arrest and stroke over five years.
People whose uric acid levels sharply declined even further—to below 5 mg/dL—saw a 23% drop in risk.
Achieving target levels was also associated with increased five-year survival rates, with the maximum benefits seen in patients already at increased cardiovascular risk.
Senior researcher Dr. Abhishek of the University of Nottingham stated, “The findings of our study are very positive and show that patients with gout who were prescribed urate-lowering drugs and achieved serum urate levels of lower than 6 mg/dL within 12 months had a much lower risk of a heart attack or stroke over the next five years.”
“Previous research from Nottingham showed treat-to-target urate-lowering treatment prevents gout flares. This current study provides an added benefit of reduced risk of heart attack, stroke and death due to these diseases,” Abhished added.
The benefits may stem from minimised inflammation, as gout is linked to chronic low-grade inflammation that can contribute to cardiovascular disease.